Belief
- Belief is an internal feeling that something is true, even if it is unproven or irrational; things we hold to be true. Belief is the simplest form of mental representation and, therefore, the building block of our thought process.
- Beliefs are the ideas, viewpoints and attitudes of a particular individual/group/society. They consist of fables, myths, folklore, traditions, and superstition. They can also be true and verifiable facts, history or legends.
- Beliefs lay the foundation of a cultural group, but they are often invisible to the group that holds them. They are important because they give us hope. A human being thrives on what he/she believes in.
- However, beliefs can be challenged. Peripheral beliefs can also be changed. Two people might have different beliefs about a phenomenon – as simple as a glass being half empty or half full, to complex theological questions such as how did earth or life come to be? Beliefs evoke emotions, but not-necessarily actions
- Belief is also referred to as cognition.
- Belief can be-
- Peripheral (weak) and
- Core (strong)- Beliefs formed by direct interaction are strong, such as for patriarchs, women are weak.
Value
- Value= Belief + Emotions
- Values are the inbuilt mechanism of an individual or a group to decide what is right or wrong. Or,
- Values are what is considered ‘important’ by an individual/society/organization. Or,
- Values are important and lasting beliefs or ideas within an individual/Society about what is good or bad and desirable or undesirable.
- Values are gathered through external environment, family, as well as experiences.
- Value denotes the degree of importance of something (or even an action). Values help in determining what actions are best to do.
- Values are ‘beliefs’ about ‘what is important
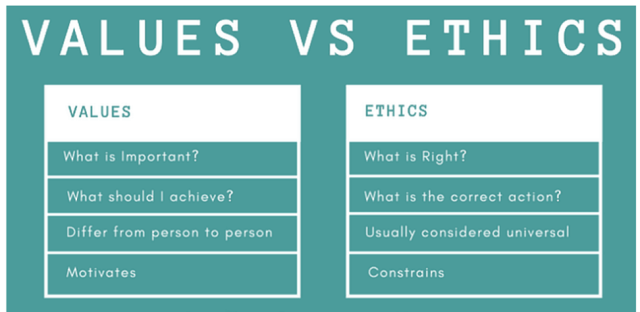
Values Vs Ethics